Kinematics in One and Two Dimensions
Kinematics in One and Two Dimensions: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, 2D Motion, Uniformly Accelerated Motion, Reaction Time Calculation under Constant Acceleration & Observer and Escalator Problems etc.
Important Questions on Kinematics in One and Two Dimensions
The figure shows the graph of a particle moving in a straight line. Starting from rest, the time after which the particle returns to its starting position is

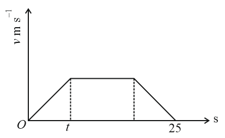
The velocity-time graph of the particle moving along a straight line is shown. The rate of acceleration and deceleration is constant and it is equal to . If average velocity during the motion is , then find the value of
An object moving with uniform acceleration has a velocity of in the positive direction when its coordinate is . If its coordinates later is , what is its acceleration?
At a distance from the traffic light brakes are applied to a locomotive moving at a velocity . Determine the position of the locomotive relative to the traffic light minute after the application of the brakes if its acceleration is .
A body of moves in the plane under the action of a force given by Assuming that the body is at rest at time the velocity of the body at is:
A bus is moving on a straight road towards north with a uniform speed of turns through anticlockwise. If the speed remains unchanged after turning , the increase in the velocity of bus in the turning process is:
The position vector of a particle is The velocity of the particle is:
A body starts from rest, what is the ratio of the distances traveled by the body during the 4th and 3rd seconds?
A body dropped from top of a tower falls 40 m during the last two seconds of its fall. The height of tower is
A car moves a distance of 200 m. It covers the first half of the distance at speed and the second half of distance at speed v. The average speed is . Find the value of v
A bus travelling the first one third distance at a speed of , the next one third at and the last one – third at . The average speed of the bus is
A particle covers half of its total distance with speed and the rest half distance with speed . Its average speed during the complete journey is
A body is moving with velocity towards east. After 10 seconds its velocity becomes towards north. The average acceleration of the body is
A boy standing at the top of a tower of 20 m height drops a stone. Assuming the velocity with which it hits the ground is
A car covers the first half of the distance between two places at and other half at . The average speed of the car is
A particle moves a distance x in time t according to equation The acceleration of particle is proportional to:
A particle has initial velocity and has acceleration Its speed after 10 s is:
A ball is dropped from a high rise platform at, starting from rest. After another ball is thrown downwards from the same platform with the speed . The two balls meet at, . What is the value of ? (Take, )
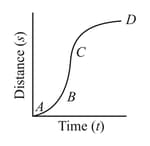
A particle shows distance–time curve as given in this figure. The maximum instantaneous velocity of the particle is around the point:
A car moves from X to Y with a uniform speed and returns to X with a uniform speed . The average speed for this round trip is
